Tests conducted by Rx Networks and the European GNSS Agency (GSA) confirm that Galileo provides real added value to citizens using Location Based Services (LBS). When used in addition to GPS and/or GLONASS, Galileo proved to significantly improve accuracy in challenging environments.
Rx Networks, a leading mobile location technology and services company, measured the performance of Galileo when used in various combinations with GPS and GLONASS. Conducted in such real-world environments as urban canyons and indoors, each test consisted of a three hour data capture of the GNSS signals which was later replayed to produce hundreds of fixes using a multi-constellation GNSS receiver from STMicroelectronics.
These difficult environments pose significant challenges in regards to location accuracy due to multipath and obstructed views of satellites.
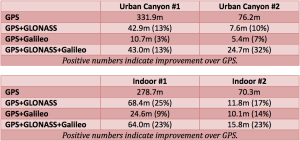
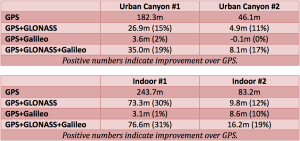
The results showed that adding Galileo on top of GPS and GLONASS (widely available in smartphones today) improves the accuracy of location fixes when indoors or in urban canyons. As expected, the GPS+Galileo combination did not exceed the performance of GPS+GLONASS, due primarily to there only being four Galileo satellites available at the time of the testing. The performance of Galileo with GPS or other GNSS will further improve in the future, as more Galileo satellites are launched.
This improved accuracy will have a profound impact across numerous sectors, including critical situations like E-112 calls. With the European Commission evaluating the mandate of GNSS location on mobile phones for emergency calling purposes, the test results demonstrate the benefit of including Galileo.
According to Gian Gherado Calini, Head of Market Development at the GSA, the agency is very happy with the results. “Dual-constellation GNSS designs are the standard for many smartphones and other devices,” he said. “The combination of GPS and Galileo provides a robust solution and is expected to offer performance that will meet or exceed end-user expectations.”
Adrian Stimpson, Senior Vice-President of Sales and Marketing, Rx Networks commented “We were delighted to offer our experience to the GSA and conduct these tests. The results should be encouraging to any GNSS chipset manufacturer who is considering adding Galileo as a competitive differentiator.”
The tables show the summary results for various scenarios and constellation combinations. The GPS row shows the absolute 2D errors in meters. All other rows show the improvement (+) or degradation (-) in meters and percentages relative to GPS-only fixes. All measurements are within the 95th percentile.
As part of the program, Rx Networks upgraded its Global Reference Network to include support for Galileo. Follow up tests are planned once the full Galileo constellation is available.